Using CellML to create multiscale models of the gut
Alberto Corrias' career with CellML began with his PhD thesis at the National University of Singapore. During this time he developed a multi-scale computational modelling framework of gastric electrophysiology, including novel cellular models of a gastric smooth muscle cell and interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC). Like John Davidson, Alberto chose to implement his cell models in CellML to allow him to easily embed these cells in a larger, multi-scale model (using CMISS).
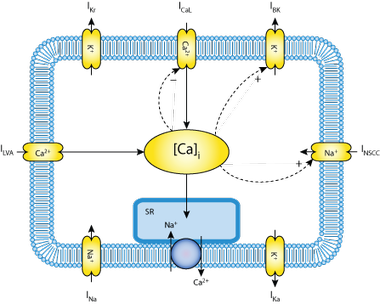
Smooth muscle cell
His gastric smooth muscle cell model was kept relatively simple to make it computationally efficient, and therefore suitable for embedding within multicellular simulations.
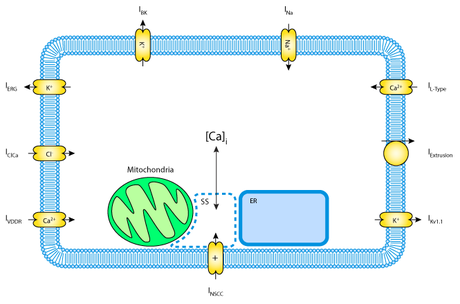
Interstitial cells of Cajal
Alberto's second, ICC model, describes the cellular processes that lead to the generation of slow wave activity in the stomach.
From the gut to the heart
More recently Alberto has moved to the University of Oxford, UK where he has joined the preDiCT project. The main aim of the preDiCT project is to model, simulate, and ultimately predict the impact of drugs on the heart's rhythm.